Ukrainian Jews, scarred by a bloody history, find themselves refugees once again

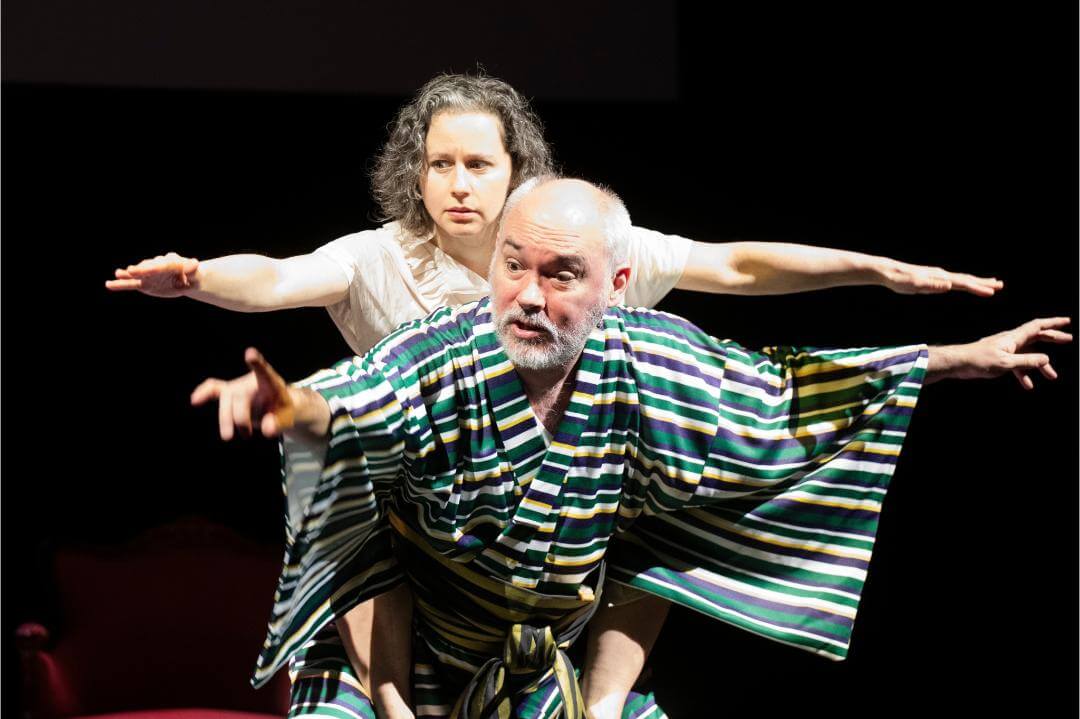
Jews from Ukraine arrive at a Jewish community center in Chisinau, Moldova, Feb. 25, 2022. (Courtesy of Rabbi Pinchas Salzman)
(JTA) — Across Ukraine, Jews are engaging in a historically Jewish experience: becoming refugees.
And hundreds of them from Odessa have headed to an unlikely destination, the impoverished nation of Moldova whose capital, Chisinau, was the site of a major pogrom that became a symbol of Jewish flight Eastern Europe in the early 20th century.
As Russian troops pour into Ukraine and bomb its cities, many Ukrainians are on the move both internally and in an attempt to leave for other countries. Border crossings in the country’s west and south are attracting thousands of prospective exiles, according to the Guardian. There are also at least 100,000 internally displaced persons.
Some of the Jews who live in Ukraine — who number at least 43,000 and potentially many more — are part of that unfortunate migration.
“We just put many mattresses in the strongest part of the sturdiest building. It will have to do for now,” Moshe Azman, one of several men bearing the title of chief rabbi in Ukraine, told the Jewish Telegraphic Agency about what is happening at the residential compound near Kyiv that Azman and his community first set up in 2014 to aid Jewish refugees fleeing the last Russian invasion.
Named Anatevka — a reference to the fictional hometown of Tevye the Dairyman from the famed Broadway musical “Fiddler on the Roof” and the iconic Sholom Aleichem short stories on which it was based — the compound has seen dozens of families arrive from more densely populated areas, Azman said.
Many of the internally displaced are from cities, some of which have been hit by Russian armaments over the past 24 hours, and are leaving for places seen as less likely to draw fire and to avoid being in crumbling Soviet-era apartment building during bombings, Azman explained.

Jewish refugees at Anatevka celebrate the opening of the community’s new synagogue on Feb. 29, 2016. (Courtesy of Rabbi Moshe Azman)
Anatevka, built at a time of a more limited Russian incursion, has no bomb shelters.
More than 100 people have died in bombings and hostilities so far in the war, which has not included significant urban fighting. In one case, one person died and five were wounded when an explosive device detonated near the center of Uman, a city of about 80,000 halfway between Odessa and Kyiv. Some parts of the city — which in peacetime is a destination for Jewish pilgrims from abroad — were evacuated following the incident, according to some reports.
The explosion happened about a mile from the gravesite of Rabbi Nachman of Bratslav, an 18th-century luminary and the founder of the Breslov Hasidic movement. Each year around Rosh Hashanah, about 30,000 Jews gather at the gravesite. Over the years, hundreds of Breslov followers, mostly from Israel, settled in Uman, which today has a year-round Jewish population of about 200.
Dozens of them, including some women and children, have left since the invasion, and a video posted to Instagram showed a bus full of Orthodox Jews being transported within the city.
But others are staying put, Chaim Chazin, a Jewish resident who moved to Uman from Israel, told JTA. His wife and daughters have been in Israel for several weeks.
“The situation is complicated right now,” he said. “All of us, everyone in Ukraine, need to literally keep our heads down until this passes.”
Elisha Shlomi, another Israel-born resident of Uman, told JTA that the remnant community intends to stay but will move to another country if fighting approaches or erupts in Uman. He declined to share where he planned to go.
As tensions between Ukraine and Russia began escalating in November, some Israeli officials said they were preparing for a wave of mass immigration from Ukraine, where at least 200,000 who are eligible to immigrate to Israel under its Law of Return for Jews and their relatives, according to a 2020 demographic study of European Jewry.
So far, the wave has not materialized on the scale that officials said they expected. But the Israeli embassy, which relocated, along with other foreign embassies, from Kyiv to Lviv in the country’s west, this month has registered appeals from about 3,000 Ukrainians who are not already citizens of Israel to immigrate to it.
Another 5,000-odd appeals connected to reaching Israel came from people in Ukraine who are already citizens, the embassy said, according to Ynet. Most of the non-citizens who contacted the embassy are married to citizens.
On Friday, Yair Lapid, Israel’s minister of foreign affairs, tweeted exit routes from Ukraine that he said were still viable for Israelis living in the country — into Poland, Romania and Hungary, all of which are absorbing an influx of refugees.
In recent days, tens of thousands of people have poured over the border from Ukraine into Moldova, a landlocked country between Romania and Ukraine that is often described as Europe’s poorest. Among them are hundreds of Jews from the vicinity of Odessa, whose residents normally enjoy one the highest standards of living anywhere in Ukraine.
The Jews who crossed over to Moldova had more help than the non-Jewish new arrivals, who mostly have come from southern Ukraine, thanks to the mobilization of some Moldovan Jews for their Ukrainian coreligionists.
“The refugees and their children are being housed in motels, and provided with hot food and essential supplies” by the local community, partly thanks to funding of the Nacht Family Foundation, a charity set up by the Israeli entrepreneur Marius Nacht and his wife Inbar, Moldova’s Chief Rabbi Pinchas Salzman said in a statement Friday. Salzman said he expected hundreds more Jewish refugees to arrive in the coming days.
They will encounter a rapidly growing infrastructure to accommodate people displaced by the war in Ukraine. IsraAID, an Israeli nonprofit humanitarian aid organization, is sending a team to the region to assist refugees. So is United Hatzalah, the Israeli emergency service that frequently assists in disasters internationally. And the Chabad house in Chisinau is preparing for a first Shabbat with an influx of Jewish refugees, though without the supply of kosher food normally imported from Odessa.
“With more people you have to be ready with food,” Rabbi Zushe Abelsky told the Los Angeles Times from the United States, where he is currently. “Our rabbis over there are also in distress.”
—
The post Ukrainian Jews, scarred by a bloody history, find themselves refugees once again appeared first on Jewish Telegraphic Agency.
A message from our Publisher & CEO Rachel Fishman Feddersen

I hope you appreciated this article. Before you go, I’d like to ask you to please support the Forward’s award-winning, nonprofit journalism during this critical time.
We’ve set a goal to raise $260,000 by December 31. That’s an ambitious goal, but one that will give us the resources we need to invest in the high quality news, opinion, analysis and cultural coverage that isn’t available anywhere else.
If you feel inspired to make an impact, now is the time to give something back. Join us as a member at your most generous level.
— Rachel Fishman Feddersen, Publisher and CEO