The real story behind ‘One Life,’ the movie starring Anthony Hopkins as Nicholas Winton, who rescued Jewish children from the Nazis
The new feature film dramatizes the story of a British stockbroker who helped 669 children escape the Nazis in Prague
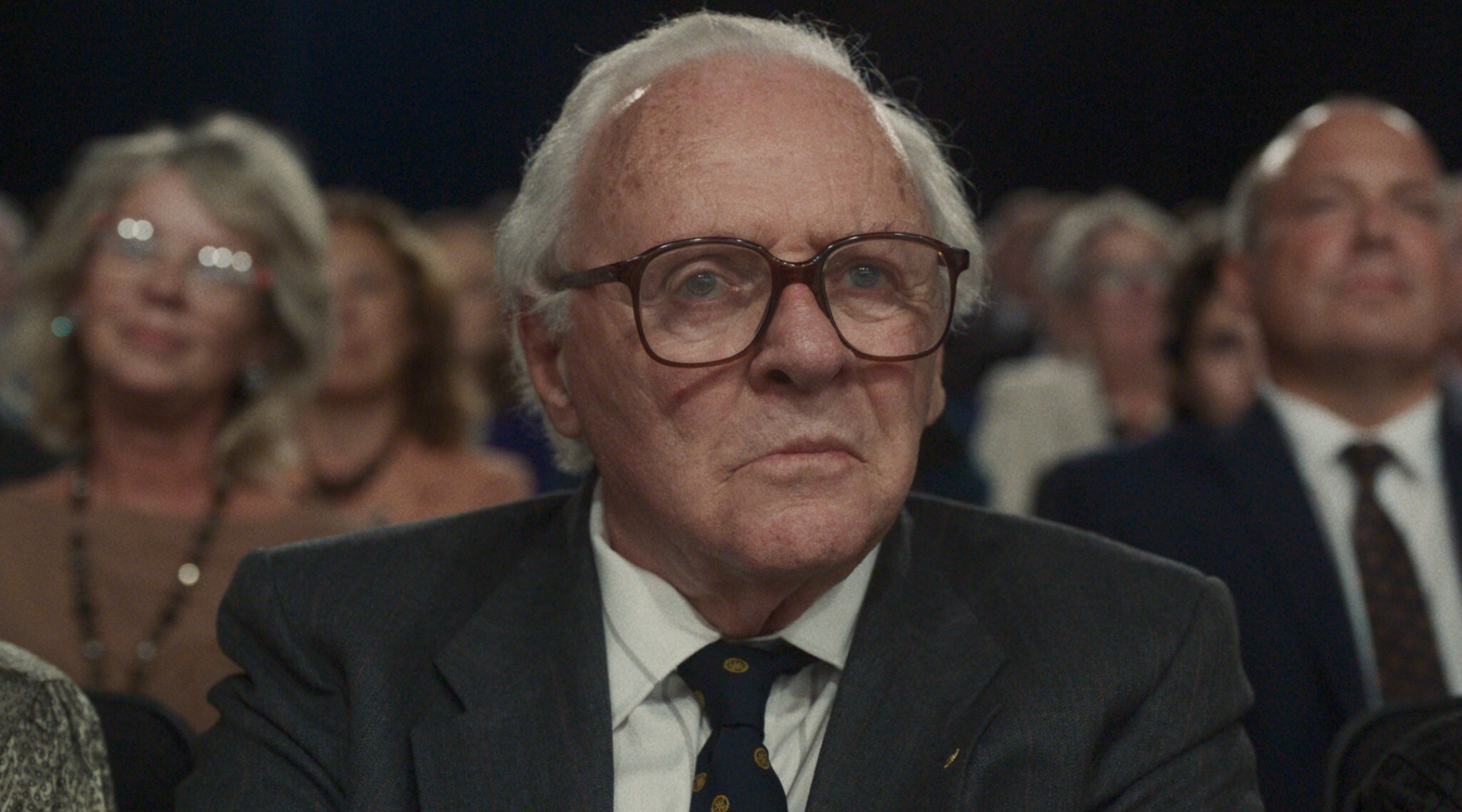

Anthony Hopkins as Nicholas Winton in “One Life”. (Peter Mountain/See Saw Films)
(JTA) — In a 1988 episode of the British television show “That’s Life,” British stockbroker Nicholas Winton was invited to sit in the audience as host Esther Rantzen dramatically revealed to him that the entire crowd was composed of the Jewish children — now adults — he had saved during the Holocaust.
That tear-jerking clip periodically goes viral on social media, but now, Winton’s story is coming to bigger screens — in a dramatic film, “One Life,” where he is portrayed by two-time Academy Award-winning actor Anthony Hopkins.
Hopkins was the casting choice of Winton’s daughter, who died as it was being filmed, seven years after her father. Already, the movie has ignited criticism — and swift revision — over promotional materials that did not include language about the children’s Jewish identities. The full story about the film’s subject is even more complex, with connections to Ghislaine Maxwell, a gold ring, the Talmud and of course the tragic saga of European Jewry.
Winton’s role in that saga was hardly assured. Born to German-Jewish parents in London in 1909, Winton (originally “Wertheim”) was baptized into the Anglican Church, and as an adult, never subscribed to any religion
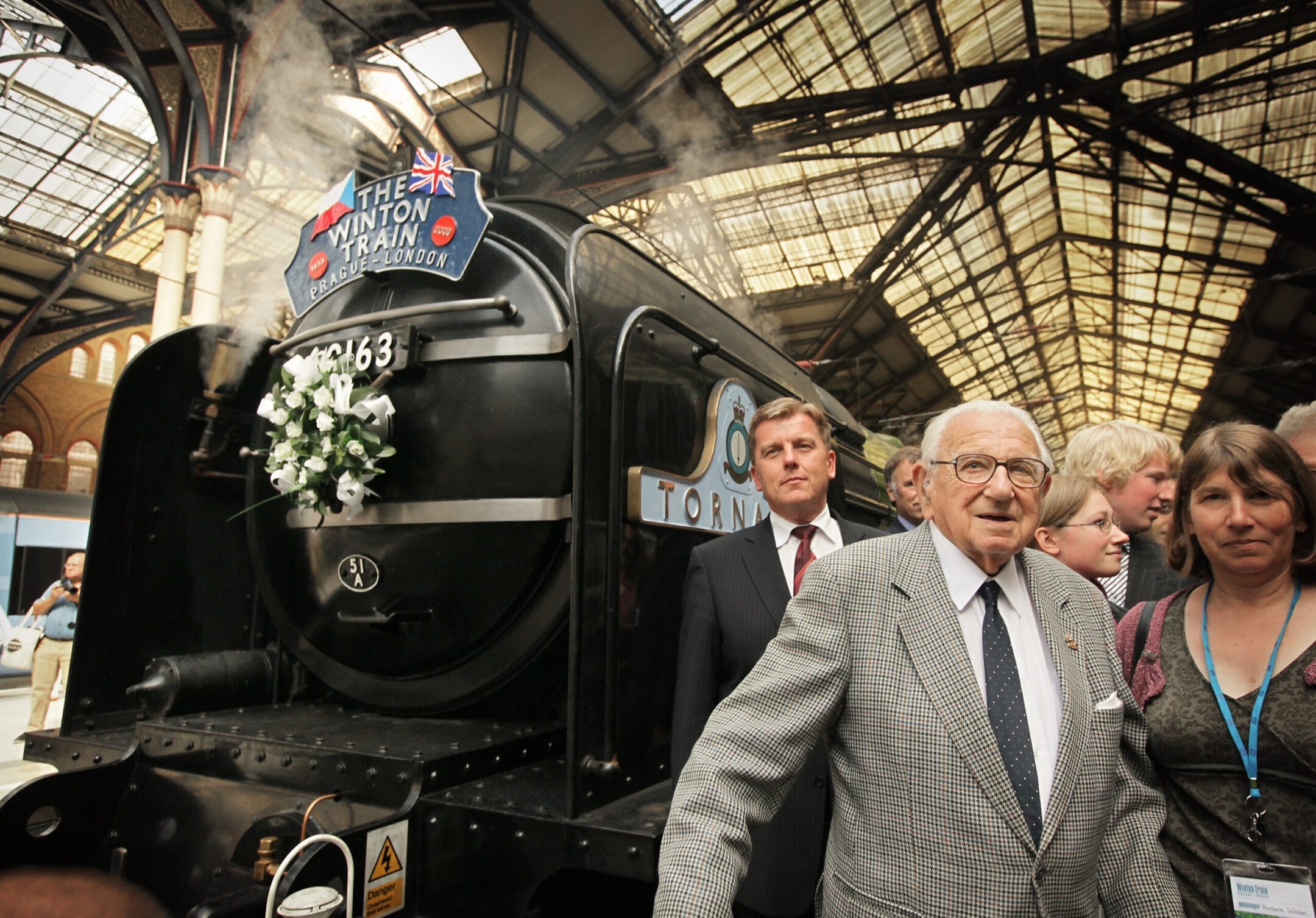

Sir Nicholas Winton stands in front of the Tornado steam train that brought evacuees in 1939 to Liverpool Street railway station on September 4, 2009 in London, England. (Peter Macdiarmid/Getty Images)
At 29, he was a stockbroker planning to ski in Switzerland with friends when his travel partner, schoolteacher Martin Blake called and said the trip was off — he was heading to Prague instead.
“I have a most interesting assignment and I need your help,” Winton recalled Blake saying. “Come as soon as you can. And don’t bother bringing your skis.”
Blake was working with the British Committee for Refugees from Czechoslovakia, an organization established to save Jews and other minority groups targeted by the Nazis in the recently-annexed Sudetenland.
But it was the appeal of a Czech Jewish social worker and activist, Marie Schmolka, that ultimately brought Winton into the Czech Kindertransport-inspired project organized by British university lecturer Doreen Warriner. Schmolka, who is not often mentioned in accounts of Winton’s efforts and is not portrayed in the movie, had visited the areas where refugees were concentrated and collected evidence to garner public support, pleading to foreign ambassadors based in Prague and to Jewish agencies abroad, hoping someone would take them in. But Britain would only take unaccompanied children.
Back in Britain, still working his job at the stock exchange, Winton and his assistants and his mother fundraised, collected or forged the children’s travel documents, and also placed advertisements in newspapers to find them foster homes.
On March 14, 1939, the day before Nazi Germany invaded the Czech regions of Bohemia and Moravia, the first of eight trains containing 669 children, mostly Jewish, headed to Britain. A ninth train was scheduled to depart on Sept. 3, but was halted — Germany had invaded Poland two days earlier, officially starting the war, and the borders were closed. None of the approximately 250 children on that train are known to have survived.
Early in the war, he worked for the Red Cross as an ambulance driver in France and in England during the London Blitz, later joining the Royal Air Force training pilots and documenting the destruction he saw with his photography. In the years after the war, he joined the International Refugee Organization, working on the repatriation of Nazi-looted goods.
His work with the children went unnoticed for decades. Then, in the late 1980s, Winton’s wife Grete Gjelstrup discovered a scrapbook in the attic with the children’s names and photos, as well as letters written by their parents.
“I suppose there are quite a number of things that husbands don’t tell their wives,” Winton told Matej Minac, who directed several films about his story.
Gjelstrup brought the book to Holocaust historian Elizabeth Maxwell, the wife of media magnate Robert Maxwell (also the parents of Ghislaine Maxwell, sentenced to prison over her role in Jeffrey Epstein’s sex abuse ring) who brought Winton’s story of saving the hundreds of children to the press, and eventually, to “That’s Life!” where he met some of the children he saved.
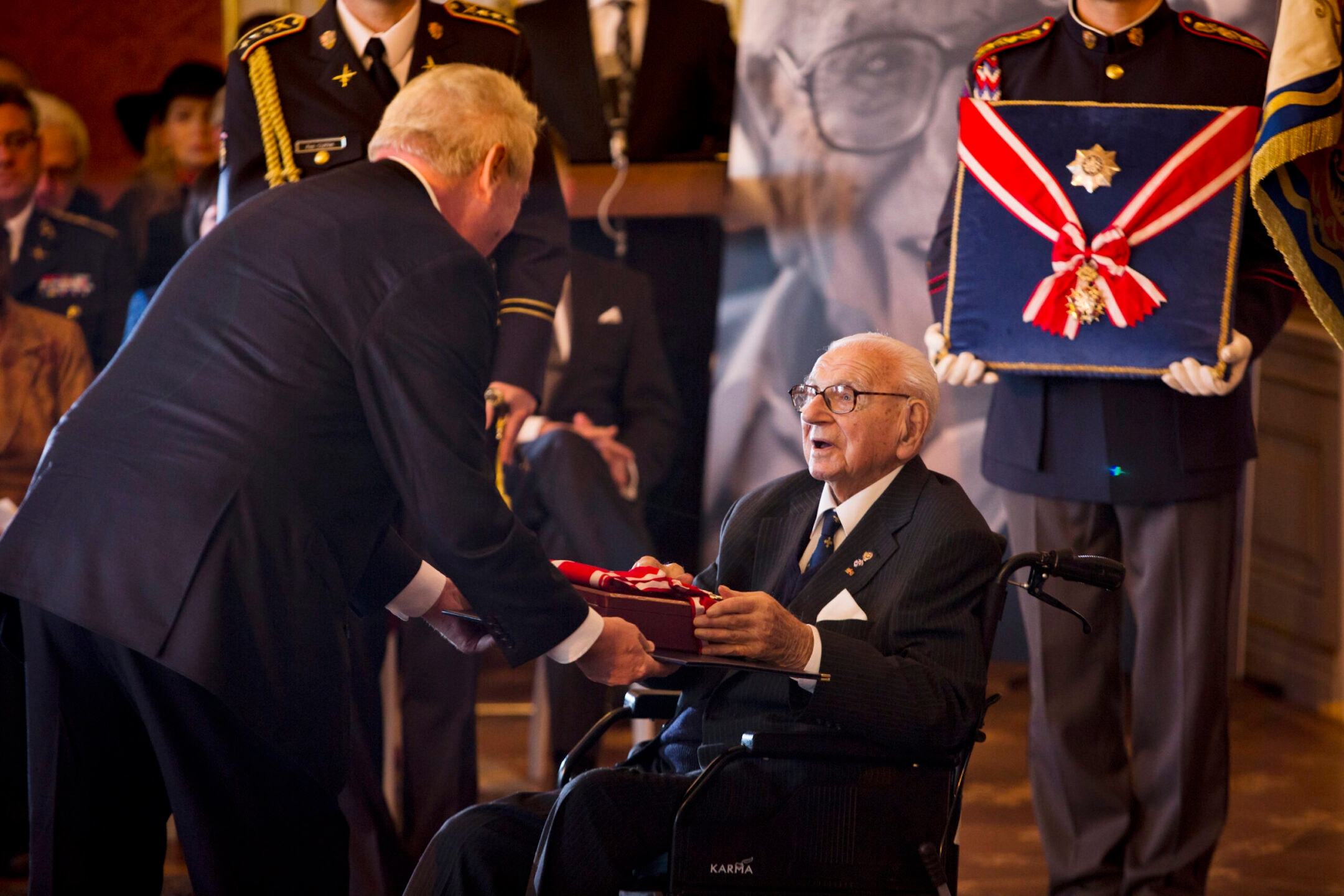

Nicholas Winton, then 105, receives the Order of White Lion, the highest order of the Czech Republic, from Czech President Milos Zeman during the Independence Day at Prague Castle, Oct. 28, 2014. (Matej Divizna/Getty Images)
Winton was nicknamed “the British Schindler” after German industrialist Oskar Schindler, who saved some 1,200 Jews during the Holocaust. More than 6,000 children and grandchildren of the Czech Kindertransport owe their lives to Nicholas Winton, according to “One Life,” the 2014 book written by his daughter and biographer, Barbara Winton, which inspired the film. (The book was originally called “If It’s Not Impossible.”) Some of their descendants appear as extras in the “That’s Life!” scene.
Upon giving permission for a film adaptation of her book, Barbara Winton made one request of the project: cast Hopkins as her father.
Barbara Winton gave the filmmakers access to her father’s letters and other archival materials.
She died in September 2022, while “One Life” was still filming.
“One Life” is a reference to a paraphrased quote from the Mishnah: “Save one life, save the world,” which was inscribed in a gold ring presented to Winton in 1988 at a Holocaust conference organized by Elizabeth Maxwell at Oxford by some of the children he saved. Winton wore the ring for the rest of his life.
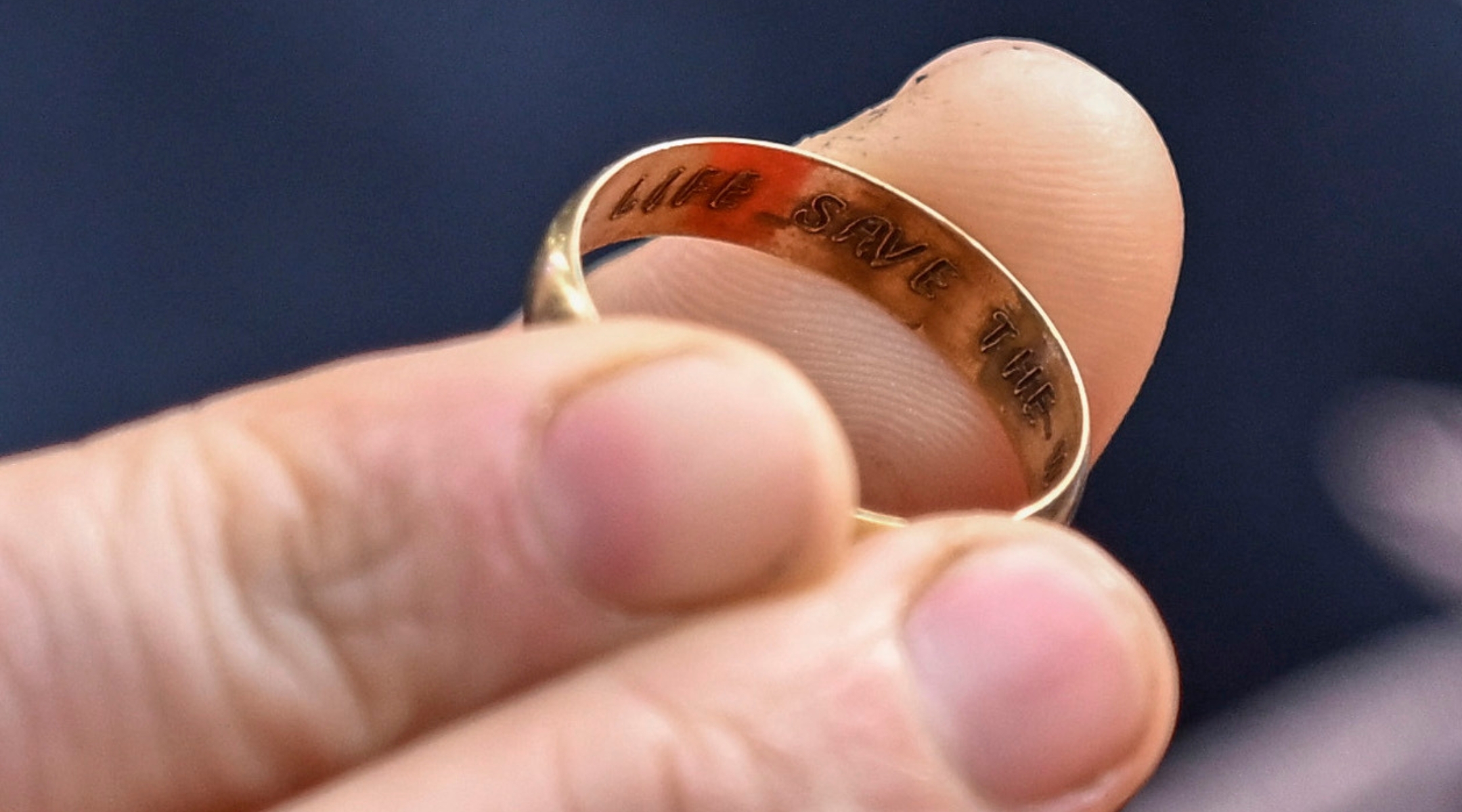

The gold ring presented to Nicholas Winton, inscribed with the phrase, “Save one life, save the world.” (Gareth Cattermole/Getty Images for BFI)
The quote is also referenced in the 1993 Steven Spielberg film “Schindler’s List” in a scene where, at the end of the war, the Jews Schindler saved give him a gold ring made from their dental fillings inscribed with a nearly identical quote as a parting gift. The real ring, according to Jozef Gross, the jeweler who created it, did not have an inscription.
Controversy arose in early January when the film’s promotional materials in the United Kingdom failed to mention that the majority of the children in danger were Jewish. Instead, some marketing materials referred to the children as “Central European.”
After social media backlash, IMDb, the Warner Bros. U.K. website, and British theater chain Vue have all changed their summary of the film to read “predominantly Jewish.”
The National Portrait Gallery in London, which was running a series of portraits of children saved by Winton as an accompaniment to the film, also changed the text in its description.
“Our Gallery’s curatorial team made this update to the website copy to better reflect the identity of the individuals who traveled on the Kindertransport,” a representative from the National Portrait Gallery wrote in an email to the Jewish Telegraphic Agency. “The original copy assumed that this was implicit, given the nature of the digital exhibition, however, following feedback, we felt it was important to clarify this.”
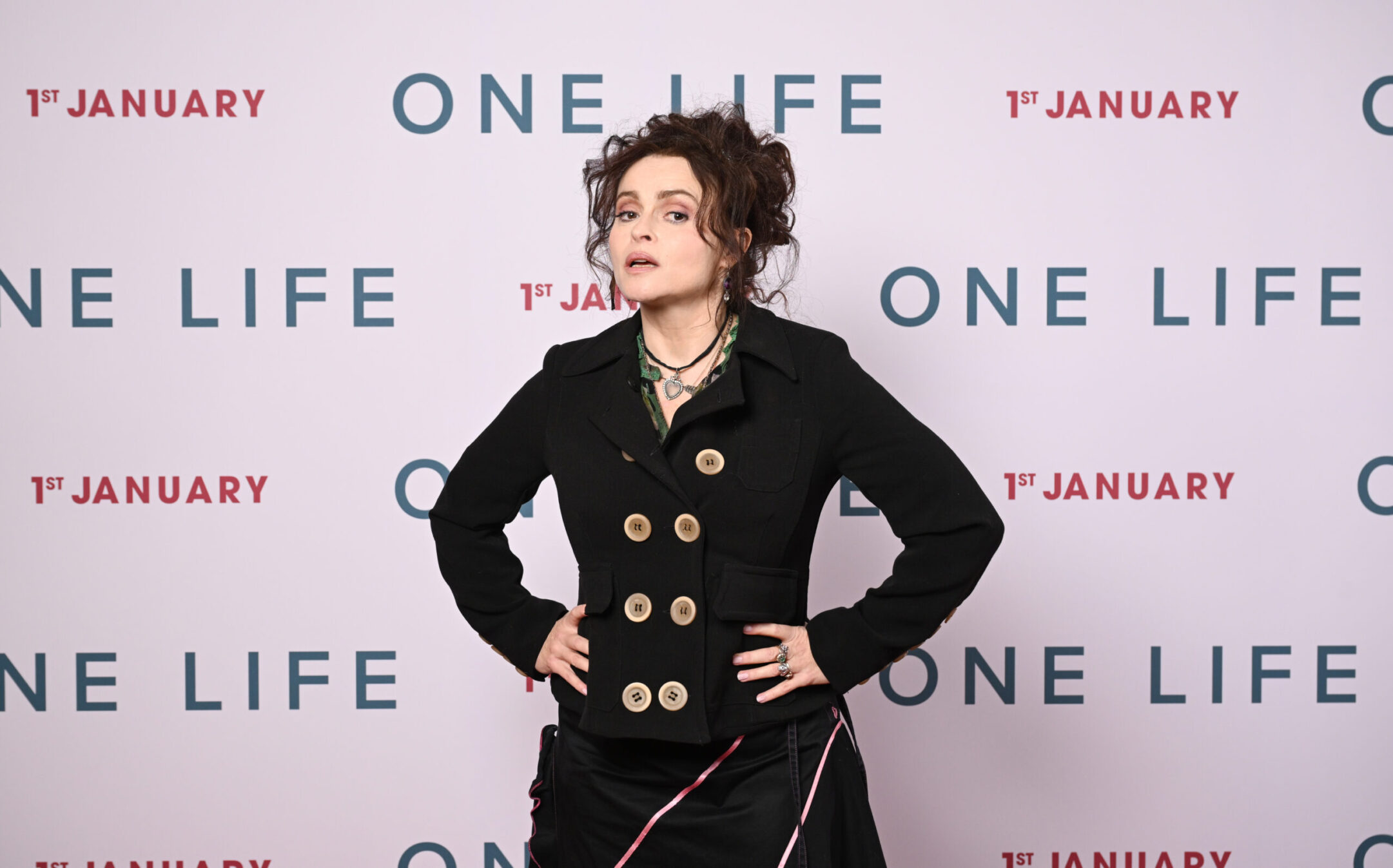

Helena Bonham Carter attends a photo call for “One Life,” out in January 2024, at The Rosewood Hotel on Nov. 30, 2023 in London. (Jeff Spicer/Getty Images for Warner Bros)
The film has another Jewish angle to it as well — actress Helena Bonham Carter, who is of Jewish descent, plays Winton’s mother, Babette Wertheim.
“It was in my DNA to play this role because I come from Austrian Jewish heritage,” Bonham Carter told the Jewish News of London. “And on top of that, on both sides, both my grandparents helped a lot of Jewish people with visas to get out of Nazi Europe.”
Bonham Carter called Winton a hero, and said the most important part of the film was to make sense of him, “what made this man, this exceptional man, so modest, do the most extraordinary things,” she said.
Nicholas Winton died in 2015 at the age of 106.
Despite going decades without recognition for his heroism during the war, the later years of his life were filled with honors and awards. Winton was knighted by Queen Elizabeth II in 2003 for his efforts during the war, and he received the Order of the White Lion, the highest order from the Czech Republic in 2014. He even had a minor planet named after him.
Still, he insisted for years that his work was not heroic.
“I was never in any danger,” Winton told a British newspaper in 2011. “I took on a big task, but did it from the safety of my home in Hampstead.”
This article originally appeared on JTA.org.
A message from our Publisher & CEO Rachel Fishman Feddersen

I hope you appreciated this article. Before you go, I’d like to ask you to please support the Forward’s award-winning, nonprofit journalism so that we can be prepared for whatever news 2025 brings.
At a time when other newsrooms are closing or cutting back, the Forward has removed its paywall and invested additional resources to report on the ground from Israel and around the U.S. on the impact of the war, rising antisemitism and polarized discourse.
Readers like you make it all possible. Support our work by becoming a Forward Member and connect with our journalism and your community.
— Rachel Fishman Feddersen, Publisher and CEO