Paying Tribute to Dr. Eugene Braunwald, Pioneer in Medicine

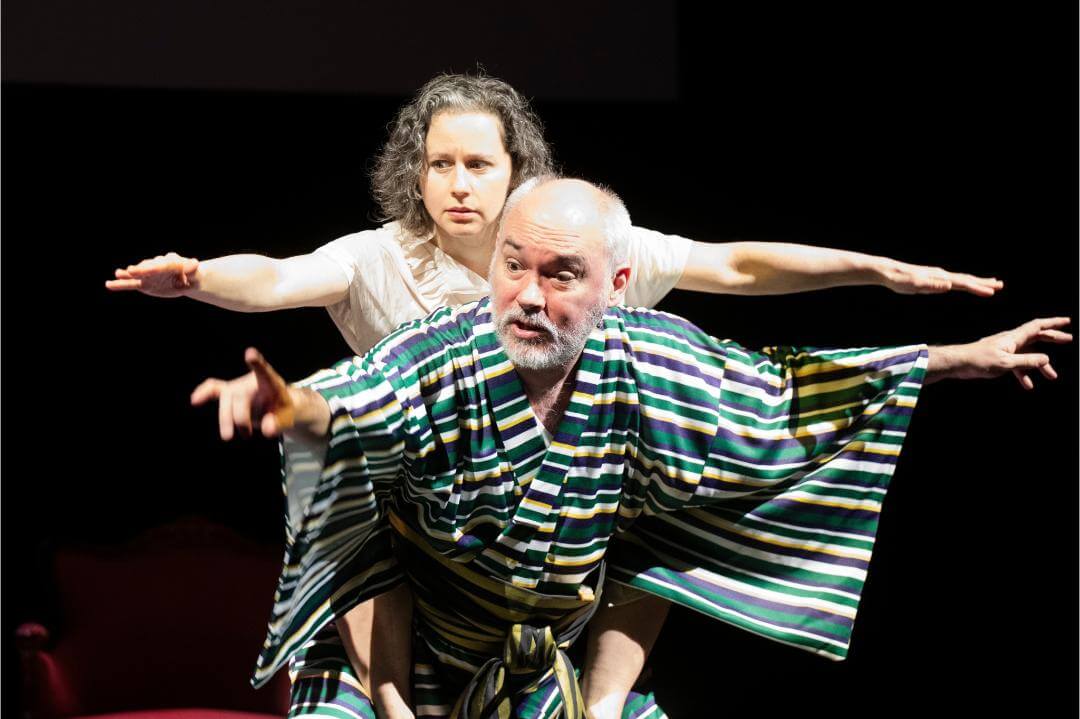
Heart of Jewishness: Dr. Eugene Braunwald, who is the subject of a new biography by Thomas H. Lee, has been called the father of modern cardiology. Image by HARVARD UNIVERSITY PRESS
● Eugene Braunwald And the Rise of Modern Medicine
By Thomas H. Lee
Harvard University Press, 400 pages, $35
The degree to which our contributions are a product of our era and the people surrounding us as opposed to our own initiative and innovation is usually difficult to discern. But Dr. Eugene Braunwald’s contributions to cardiology in the latter half of the 20th century are unparalleled by any standard. Braunwald, who turned 84 in August, wrote more than 1,000 academic articles and penned a meticulous cardiology textbook, “Braunwald’s Heart Disease Review and Assessment: Expert Consult” (you can purchase the ninth edition, which is officially written by other authors, at your favorite seller). His work to understand cardiac function and dysfunction, and his many innovations, have helped millions who struggle with heart disease.
“Eugene Braunwald and the Rise of Modern Medicine,” by the Harvard University professor Thomas Lee, examines the trends and political factors that affected Braunwald’s work and the science that surrounded it. Lee, a physician and occasional mentee of Braunwald, is especially skilled at moving effortlessly — from a telephoto lens focused on Braunwald’s life to wider-angle examinations of larger national trends, such as our technical optimism during the space race, or behind the scenes political negotiations that led to doubled and tripled funding for the National Institutes of Health in the 1950s.
Lee masterfully describes the inner workings of numerous hospitals and laboratories, as well as the political forces that shaped medicine during Braunwald’s life. There are consistent themes, including a tension between hopelessness and audacity and the influence of politics and wars on medical research. For example, Braunwald left NIH to chair the department of medicine at UC San Diego in the late 1960s.
Braunwald had been promised a hospital, a key training ground for his young physicians, but Ronald Reagan took a draconian approach to higher education, firing the president of UC Berkeley immediately after winning the California governorship retaliations, purportedly, for the lenient administrative approach to protests against Vietnam and pushing for cuts to the entire UC educational system. All this delayed the construction of the hospital dramatically.
Braunwald was born in Vienna in the shadow of the Nazis’ rise to power. Lee includes a gripping description of his mother’s clever intervention with a Nazi SS captain that saved Braunwald’s father’s life in 1938. After stops in Switzerland and London, the family was sponsored by a distant aunt and settled in Brooklyn, near many other Viennese Jews, Freud’s family among them. Despite being a hardworking and diligent student, Braunwald faced serious anti-Semitism in most medical schools. Lee includes a detailed table illustrating comparative acceptance rates for Protestants, Catholics and Jews at New York colleges of medicine; however, eventually he was accepted to New York University.
Braunwald’s career included work at a number of New York hospitals, NIH, UC San Diego and hospitals in the Harvard medical system. He was productive for six decades and was a key figure in the move from passive, observation of the heart to audacious interventions, including catheterizations and the use of ACE inhibitors immediately after myocardial infarction.
The degree to which this book will appeal to nonacademics and nonphysicians is unclear. Some of the book focuses considerable energy on translating Braunwald’s work for the lay reader, trying to balance engaging stories with accurate descriptions of Braunwald’s many research contributions. Lee does this skillfully, but there are still significant passages that some readers may find too dense.
There are advantages and disadvantages when physicians write about other physicians. Lee’s advantage is the keen appreciation for the pressures facing Braunwald, and a finely honed sense of the relevance of the work. And Lee succeeds at making complex cardiac issues understandable.
Unfortunately, physicians tend to focus on one another’s professional lives, and the book actually reveals very little about Braunwald’s personality or life outside of medicine. His wife, a successful surgeon, innovator and academic in her own right, disappears from the story for vast portions of the book, only to reappear suddenly later on, suffering from metastatic breast cancer. Interviews with his colleagues focus almost exclusively on his research and on his clinical or administrative skills and ideas. In addition, the book is clearly a tribute: Braunwald’s close relationship with industry, his lack of use of informed consent with vulnerable patients and his poorly conceived administrative decisions are explained in the most generous light.
Nevertheless, in the age of the sequester, those reading from the perspective of academic medicine will not miss the meteoric progress of Braunwald and his colleagues after the significant investment the nation made in the NIH, where Braunwald spent a significant portion of his young career. By providing resources to smart, motivated young researchers, the nation was paid back thousand-fold in healthier lives. How much we are losing now due to the cutting of NIH budgets, which support the early careers of promising biomedical researchers, will probably never be quantified.
Dan Shapiro is professor and chair of the department of humanities at the Penn State College of Medicine.
A message from our Publisher & CEO Rachel Fishman Feddersen

I hope you appreciated this article. Before you go, I’d like to ask you to please support the Forward’s award-winning, nonprofit journalism during this critical time.
We’ve set a goal to raise $260,000 by December 31. That’s an ambitious goal, but one that will give us the resources we need to invest in the high quality news, opinion, analysis and cultural coverage that isn’t available anywhere else.
If you feel inspired to make an impact, now is the time to give something back. Join us as a member at your most generous level.
— Rachel Fishman Feddersen, Publisher and CEO